The Technology That is Dealing a Huge Blow to International Business
The current business landscape is confronted with myriad challenges in supply chain management. Complex logistics is a daily challenge faced by companies as they attempt to track their products across continents to establish authenticity. One of the solutions that are changing the way business is done in the world is blockchain in supply chain management.
This is a high-tech solution that can help industries address decades-old issues. Businesses end up losing billions of dollars every year as a result of fraud, forgeries, and ineffective tracking systems. However, with blockchain technology, this fact is being transformed through the development of secure, transparent and traceable networks.
Retailers and manufacturers are only a few of the parties engaged in supply chains. Every step has chances of mistakes, time wastage, and conflicts. Many of these problems can be eradicated by blockchain technology which offers people one source of truth that all can use and trust.
Why is Blockchain Ideal in Supply Chains?
Blockchain technology is similar to a digital registry where all transactions are registered forever. The best way to imagine it is as a notebook that could be read by many people, but nobody could erase or modify any earlier records. This leaves an indelible trace detailing the journey of products.
Conventional supply chains are based on documents and distinct databases. This leaves loopholes in which information is lost or manipulated. Blockchain integrates everybody into a single system that is updated in real-time.
The technology employs cryptographical security to secure data. The information contained within the blocks acts as a link to the information within the prior block, forming an unbreakable chain. This ensures fraud is almost impossible and develops trust among business associates.
Complex Processes are Automated by Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing computer-written contracts. They automatically activate activities whenever certain conditions are fulfilled. An illustration of this is the release of payment upon the delivery of goods to the destination.
Such automation minimizes human error and accelerates transactions. Businesses do not have to wait until manual approvals are received or fear delayed payments. This is done automatically based on agreed upon rules.
Benefit 1: 100% Transparency Creates Trust
The implementation of blockchain in supply chain management establishes transparency in the chain like never before. All participants will be able to access relevant information on products, shipments, and transactions on a real-time basis.
This openness does away with the black box challenge, which afflicts conventional supply chains. Firms do not have to wonder where to find their products or when they will be received. Accurate information can be received by all the stakeholders at the same time.
The customers insist on knowing the origin of their products. They desire to know how they are made, how they work and how they affect the environment. Through blockchain, this information can be easily made available and verifiable.
Success Stories of Transparency in the Real World
Walmart implements blockchain to monitor foods sold at the store back to the farm. They can locate the source within seconds rather than days when there is a foodborne illness outbreak. This quick reaction prevents waste and protects consumers.
De Beers uses blockchain to monitor the movement of diamonds to avoid conflict diamonds making it to the market. Every diamond receives a digital certificate accompanying it along the supply chain. This provides a guarantee of ethical sourcing and consumer confidence.
Benefit 2: Improved Security Provides Secure Data
Breach of security is costing companies millions of dollars, and their reputations are hurt permanently. Classical databases create single points of failure which can be exploited by hackers. Blockchain is distributed across more than one node and is virtually impossible to hack.
Cryptographic verification must occur on every transaction prior to its addition to the chain. This provides several levels of security that defend against sensitive business information. The network is not compromised even when one of the nodes is compromised by hackers.
Because blockchain records cannot be changed, the information is fixed and cannot be altered in the past. When information is documented it will be included in the historical record for all time. This eliminates fraud and maintains the integrity of data.
Intellectual Property and Trade Secret Protection
Businesses spend a lot of money to develop their own processes and formulas. Blockchain is a secure way to keep this intellectual property stored and yet allow it to be shared as needed with partners. Access controls are used to ensure sensitive information is only accessed by the proper parties.
Without the risk of theft, product designs, manufacturing specifications and quality standards can be shared. This facilitates more effective cooperation while guarding valuable competitive advantages.
Benefit 3: Enhanced Product Traceability Provides Quality
Every year, product recalls cost companies billions of dollars and legal expenses. Supply chain management based on blockchain allows accurate traceability and is able to keep issues confined to a single batch or shipment.
Each product is given a special digital identity, which tracks the entire lifecycle. From raw materials all the way to final delivery there is a permanent record of each step. This provides a complete audit trail that can be verified by regulators and consumers.
Companies are able to easily detect defective products and their location when problems occur. This accuracy minimizes recall expenses and the effect on unimpacted inventory.
Pharmaceutical Industry Advantages
The problem of fake drugs penetrating the pharmaceutical industry is a serious issue. Counterfeit drugs put patients at risk and cost the sector billions of dollars a year. By using blockchain, an unbroken chain of custody is formed that helps prevent counterfeiting.
Each batch of medication receives a distinct blockchain identity which can be checked by pharmacies prior to dispensing. QR codes allow patients to scan to verify that they are using genuine medicines. Such a system ensures safety of the population and prevents doubts about pharmaceutical brands.
Benefit 4: Automated Processes Save on Costs
In old-fashioned supply chains, a lot of paperwork, verifications, and unnecessary processes are involved. Such inefficiencies add costs and slowness to the operations. Many of these processes are automated with help of blockchain using smart contracts and digital verification.
When blockchain is used to automatically process regular transactions, administrative costs are reduced considerably. It is no longer necessary to have armies of clerks to do paperwork or check transactions by hand. These tasks are carried out more quickly and more precisely with the help of digital systems.
The common accounting system removes multiple record keeping. All can access the same information, and it lowers the cost of storage and synchronization. This is a cost-effective, streamlined method.
Optimization of Inventory
Blockchain offers visibility of inventory throughout the supply chain in real time. Stock levels at all locations are instantly visible to the companies. This prevents overstocking and stock-outs that tie up capital or cause sales losses.
With smart contracts, automated reordering guarantees optimal inventory levels. New orders are triggered when stock hits predetermined levels. This lowers carrying costs and maintains service levels.
Benefit 5: Improved Compliance with Regulations
Industries are under pressure to meet growing regulatory demands on product safety, environmental protection and labor standards. Traditionally, compliance reporting involves a lot of documentation and manual audits. Supply chain systems using blockchain automatically create compliance reports based on registered transactions.
Blockchain records can be accessed by regulatory bodies who can confirm compliance. This saves money on auditing and also accelerates approval procedures. Compliance can be demonstrated at any time instead of conducting periodic checks at companies.
Environmental policies involve close monitoring of carbon emissions and waste disposal. These metrics are automatically recorded on blockchain throughout the supply chain. This facilitates proper environmental reporting and allows companies to achieve sustainability objectives.
Food Safety Rules and Regulations
Food safety laws emphasize close monitoring of temperature, handling methods and expiry dates. This information is automatically documented by blockchain through the cold chain using IoT sensors. Any temperature breach generates instant alerts to prevent spoiled food.
Organic certification involves demonstrations that goods comply with high standards during production processes. Blockchain keeps records of farming practices, processing, and handling procedures unaltered. This makes organic certification quicker and more efficient.
Benefit 6: Better Supplier Relationships and Trust
Lack of trust and poor communication processes are usually problems in traditional supplier relations. There are conflict issues like delivery terms and quality standards, and payment delays. Blockchain generates transparency that develops trust among partners.
The same information about orders, shipments and quality metrics can be seen by all parties. This transparency ensures no surprises and minimizes conflicts. When something goes wrong, all can see what happened and when it occurred.
Smart contracts are fair and equitable to everyone. When delivery conditions are met, payments are automatically released. Buyers are assured of performance and suppliers are paid promptly. This creates more cooperative relationships.
Small Supplier Empowerment
Information asymmetries can frequently be used by large corporations to control relationships with suppliers. Blockchain levels the playing field as small suppliers have equal access to the same information as large buyers. This brings more equitable negotiations and improved outcomes for all.
Blockchain records of timely deliveries and quality performance can help small suppliers demonstrate their reliability. This enables them to compete with bigger suppliers and win better contracts. The technology democratizes participation in the supply chain.
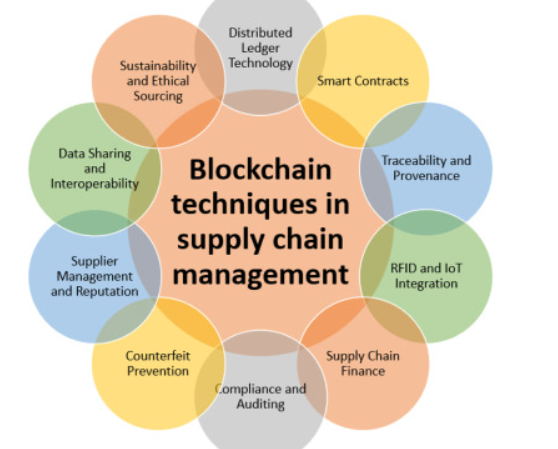
Benefit 7: Real-Time Visibility Enhances Decision Making
Business decisions are often flawed because of outdated or incomplete information. Conventional supply chains provide poor visibility of ongoing activities. Blockchain supply chain management provides real-time information that facilitates improved decision-making.
Managers are able to view inventory position, shipment status, and production status in real-time. Such visibility allows taking action ahead of issues that could affect customers. When shipments are delayed or production needs to be changed according to demand changes, companies can reroute shipments accordingly.
The detailed information from blockchain enables complex analytics and artificial intelligence capabilities. It allows companies to detect patterns, anticipate issues, and optimize operations using complete historical data. As emerging technologies continue to evolve, innovative companies are leveraging advanced AI and blockchain solutions to create more intelligent and responsive supply chain networks.
Predictive Analytics Capability
Historical blockchain statistics can be used to create advanced predictive algorithms. By analyzing previous sales volumes and seasonal fluctuations, companies can make better predictions about demand. This lowers inventory expenses and increases service levels.
Machine learning algorithms are able to spot early warning signs of supplier issues. When quality measures drop or delivery times worsen, automatic warnings can be sent. This facilitates proactive supplier management and helps avoid supply disruption.
Benefit 8: Prevention of Fraud and Counterfeiting
Counterfeiting costs the world economy more than $500 billion every year. Counterfeit products harm consumers, negatively affect brand image, and reduce legitimate sales. Blockchain can establish an immutable list of legitimate goods that cannot be faked by counterfeiters.
Every original product is assigned a unique blockchain identity that is verifiable by consumers. Physical products are connected to their blockchain records via QR codes or NFC chips. Customers can establish authenticity instantly before making purchases.
Fraud can be identified far easier with blockchain records because they are immutable. Any attempts to manipulate documentation leave an indelible mark on records that can be tracked by investigators. This deters fraud and assists in prosecuting criminals.
For more detailed information about blockchain security measures and anti-counterfeiting technologies, the World Economic Forum’s blockchain insights provide comprehensive analysis of how this technology is transforming global trade security.
Luxury Goods Protection
Counterfeiting hurts luxury brands more than others. There are counterfeit designer bags, watches, and other apparel in the market. Authentication through blockchain is used by luxury brands to guard their intellectual property and preserve exclusivity.
Blockchain records help customers confirm whether luxury purchases are genuine. This builds confidence in secondary markets and retains brand value. True luxury products maintain higher value when purchasers can confirm their provenance.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Although the benefits of blockchain are enormous, it requires careful planning and investment. Businesses need to revise existing systems and educate workers about new procedures. This transition can be challenging but pays off in the end.
Technical expertise is needed to integrate with current enterprise resource planning systems. Companies commonly require the services of blockchain experts to facilitate successful deployment. The investment pays dividends in terms of efficiency and cost savings.
Employee training is crucial for blockchain adoption. Employees should understand how the new system will impact their daily duties. Comprehensive training programs ensure smooth transitions and maximum benefits.
Starting Small and Scaling
Businesses should start with pilot projects to test blockchain applications. Small-scale implementations enable organizations to learn and refine processes before wholesale implementation. This minimizes risks and develops internal expertise.
Successful pilots can be extended step by step to include more suppliers and product lines. This incremental process enables firms to achieve early returns while managing implementation complexity.
Industry-Specific Applications
Blockchain can help various industries in different ways. The technology is adaptable to specific requirements and regulatory conditions. Understanding industry-specific applications enables companies to identify the most appropriate opportunities.
Manufacturing companies use blockchain to trace components through complex assembly processes. This allows quick detection of flawed components and accurate recalls. Quality control becomes more efficient and effective.
Blockchain allows retail companies to verify product authenticity and track inventory. This reduces shrinkage and enhances customer satisfaction. Supply chain transparency also supports sustainability marketing efforts.
Transforming the Agricultural Sector
Agriculture faces specific challenges such as weather risks, seasonal fluctuations, and complicated certification processes. Blockchain supply chain applications can assist farmers and food companies in addressing these challenges more effectively.
Crop insurance claims can be automatically processed based on weather data captured on blockchain. This eliminates paperwork and accelerates claim payments to farmers. Smart contracts can provide fair and transparent insurance practices.
Future Trends and Developments
Blockchain technology is rapidly evolving. New features and capabilities are emerging continuously, expanding possible applications. Business organizations must stay current with trends that may benefit their operations.
Internet of Things sensors enable integration and automatic data collection throughout the supply chain. Data on temperature, humidity and location are input directly into blockchain entries. This eliminates manual data entry and enhances accuracy.
Artificial intelligence algorithms will increasingly analyze blockchain data to optimize supply chain operations. Predictive maintenance, demand forecasting, and route optimization will become more sophisticated and precise.
Interoperability Improvements
Existing blockchain networks are often isolated. The future will allow various blockchain systems to communicate and exchange information. This interoperability will establish more comprehensive supply chain visibility.
Standards are being developed that provide standardized protocols for blockchain supply chain applications. These standards will reduce implementation costs and enhance compatibility between different systems.
Measuring Return on Investment and Success
Companies require metrics to measure the success of blockchain implementation. Traditional supply chain indicators like on-time delivery and inventory turns remain significant. Additional blockchain-specific metrics provide better understanding of system performance.
Financial gains are evident through cost savings from less paperwork, faster transactions and fewer disputes. Companies should monitor these savings to justify blockchain investments and identify areas for improvement.
Improved product availability and quality assurance frequently leads to higher customer satisfaction. Measuring retention rates and customer feedback can demonstrate blockchain’s business impact.
Key Performance Indicators
The percentage of products with complete supply chain traceability records can measure transparency achievement. This metric shows the extent of blockchain implementation comprehensiveness.
The number of counterfeiting cases prevented and detected can track fraud reduction. This indicator proves blockchain’s protective value and defends brand reputation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the cost of implementing blockchain? A: Implementation costs vary depending on company size, complexity, and platform selected. Small pilots may cost thousands while enterprise-wide implementation can cost millions. Long-term savings usually justify the investment.
Q: How long does blockchain implementation take? A: Simple pilot projects can be online within several months. Enterprise implementations typically take 12-24 months. Timeline varies with system complexity, integration needs and organizational readiness.
Q: Is blockchain compatible with current supply chain software? A: Yes, blockchain platforms integrate with existing enterprise resource planning systems, warehouse management systems and other supply chain software. APIs and middleware solutions support these integrations.
Q: Is sensitive business data safe on blockchain? A: Cryptographic encryption and distributed structure provide very high security on blockchain. The technology is more secure than traditional centralized databases and has never been successfully hacked at the protocol level.
Q: Do all suppliers need to use blockchain? A: No, businesses can implement blockchain gradually. Initial focus should be on critical suppliers and high-risk products. Network value increases with participation, though even partial implementation provides benefits.
Q: What happens if internet connectivity fails? A: Blockchain networks are distributed among multiple nodes globally. Local network outages don’t affect the entire network. Data automatically syncs when connectivity is restored.
The Future of the Business World
Blockchain supply chain management represents a fundamental shift toward more transparent, secure, and efficient business operations. Early adopters of this technology gain competitive advantages that increase over time.
The technology eliminates traditional trade-offs between transparency and security. Businesses can share necessary information while protecting sensitive data. This balance facilitates greater collaboration without sacrificing competitive positions.
As blockchain adoption increases, businesses without access to the technology may find themselves at significant disadvantages. Customers increasingly demand transparency and authenticity that blockchain can reliably provide.
Verifiable supply chain information will become a crucial consumer trust factor. Businesses that can demonstrate their sustainability claims, quality assurance and ethical conduct will attract more customers. These proofs are feasible and reliable with blockchain.
The eight strong advantages of blockchain presented in this article highlight why blockchain is becoming essential in modern supply chains. The technology addresses important business problems that have plagued companies for decades, from enhanced security to reduced fraud.
Early adopters are already receiving significant benefits from their blockchain investments. Reduced costs, improved efficiency and enhanced customer relationships justify implementation efforts. These benefits will multiply as the technology matures.
Companies cannot afford to delay planning their blockchain adoption strategies to remain competitive in the digital economy. The question is not whether organizations should adopt blockchain, but how quickly they can implement it successfully. The future belongs to companies that embrace this game-changing technology today.